💡 摘要:是否遇到过缓存数据与数据库不一致的尴尬局面?是否在数据更新后发现用户看到的还是旧数据?缓存一致性是分布式系统中最具挑战性的问题之一,它直接影响到数据的准确性和用户体验。本文将深入探讨Redis缓存一致性的各种解决方案,从简单的更新策略到复杂的最终一致性方案,帮你构建可靠的数据同步体系!
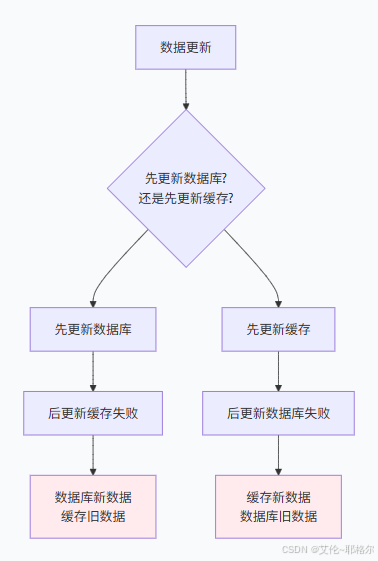
一、缓存一致性挑战
1. 为什么缓存一致性很难?
典型的不一致场景:
🕒 时序问题:缓存更新和数据库更新的顺序
⚡ 并发冲突:多个请求同时更新同一数据
🔄 操作失败:一个操作成功另一个失败
🗑️ 缓存失效:缓存过期或淘汰导致数据不一致

2. 一致性级别对比
| 一致性级别 | 描述 | 性能影响 | 实现复杂度 |
|---|
| 强一致性 | 任何时刻数据一致 | 高 | 极高 |
| 最终一致性 | 一段时间后数据一致 | 中 | 中 |
| 弱一致性 | 不保证数据一致 | 低 | 低 |
二、基础更新策略
1. Cache-Aside模式(旁路缓存)
最常用的缓存模式:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| def get_user(user_id):
user_data = redis.get(f"user:{user_id}")
if user_data:
return user_data
user_data = db.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", user_id)
if user_data:
redis.setex(f"user:{user_id}", 3600, user_data)
return user_data
def update_user(user_id, new_data):
db.update("UPDATE users SET ... WHERE id = %s", user_id, new_data)
redis.delete(f"user:{user_id}")
return True
|
问题:并发更新可能导致不一致

2. Write-Through模式(直写)
同步更新缓存和数据库:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class WriteThroughCache:
def __init__(self, redis_client, db_client):
self.redis = redis_client
self.db = db_client
def set(self, key, value, expire=3600):
self.db.update_data(key, value)
self.redis.setex(key, expire, value)
return True
def get(self, key):
return self.redis.get(key)
cache = WriteThroughCache(redis, db)
cache.set("user:1001", user_data)
|
优点:保证强一致性
缺点:写性能较低,不适合高频写场景
三、最终一致性方案
1. 延迟双删策略
解决并发冲突的方案:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| def update_user_with_double_delete(user_id, new_data):
redis.delete(f"user:{user_id}")
db.update("UPDATE users SET ... WHERE id = %s", user_id, new_data)
threading.Timer(1.0, lambda: redis.delete(f"user:{user_id}")).start()
return True
def get_user_with_retry(user_id, max_retries=3):
"""带重试的查询"""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
user_data = redis.get(f"user:{user_id}")
if user_data:
return user_data
user_data = db.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", user_id)
if user_data:
redis.setex(f"user:{user_id}", 3600, user_data)
return user_data
time.sleep(0.1 * (2 ** attempt))
return None
|
2. 基于消息队列的异步更新
使用消息队列保证最终一致性:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| import json
from kafka import KafkaProducer
class CacheAsyncUpdater:
def __init__(self):
self.producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=['kafka1:9092', 'kafka2:9092'],
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
def update_user(self, user_id, new_data):
db.update("UPDATE users SET ... WHERE id = %s", user_id, new_data)
message = {
'type': 'cache_update',
'key': f"user:{user_id}",
'data': new_data,
'timestamp': time.time()
}
self.producer.send('cache-updates', message)
return True
def cache_update_consumer():
consumer = KafkaConsumer(
'cache-updates',
bootstrap_servers=['kafka1:9092', 'kafka2:9092'],
value_deserializer=lambda m: json.loads(m.decode('utf-8'))
)
for message in consumer:
data = message.value
if data['type'] == 'cache_update':
redis.setex(data['key'], 3600, data['data'])
|
四、强一致性方案
1. 分布式事务方案
使用2PC实现强一致性:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class DistributedTransaction:
def __init__(self, redis_client, db_client):
self.redis = redis_client
self.db = db_client
def update_with_2pc(self, key, new_data):
"""两阶段提交更新"""
try:
db_transaction = self.db.begin_transaction()
db_transaction.update("UPDATE users SET ... WHERE id = %s", key.split(':')[1], new_data)
self.redis.setex(f"lock:{key}", 30, "prepared")
self.redis.setex(f"temp:{key}", 30, new_data)
db_transaction.commit()
self.redis.setex(key, 3600, new_data)
self.redis.delete(f"lock:{key}")
self.redis.delete(f"temp:{key}")
return True
except Exception as e:
if 'db_transaction' in locals():
db_transaction.rollback()
self.redis.delete(f"lock:{key}")
self.redis.delete(f"temp:{key}")
raise e
|
2. 基于binlog的同步方案
使用MySQL binlog同步缓存:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import pymysqlreplication
class BinlogSyncService:
def __init__(self, redis_client):
self.redis = redis_client
self.setup_binlog_stream()
def setup_binlog_stream(self):
"""设置binlog监听"""
stream = pymysqlreplication.BinLogStreamReader(
connection_settings={
'host': 'mysql-master',
'port': 3306,
'user': 'repl',
'passwd': 'password'
},
server_id=100,
blocking=True,
resume_stream=True
)
for binlogevent in stream:
if isinstance(binlogevent, WriteRowsEvent):
self.handle_write_event(binlogevent)
elif isinstance(binlogevent, UpdateRowsEvent):
self.handle_update_event(binlogevent)
elif isinstance(binlogevent, DeleteRowsEvent):
self.handle_delete_event(binlogevent)
def handle_write_event(self, event):
"""处理插入事件"""
for row in event.rows:
if event.table == 'users':
user_id = row['values']['id']
redis_key = f"user:{user_id}"
self.redis.setex(redis_key, 3600, json.dumps(row['values']))
def handle_update_event(self, event):
"""处理更新事件"""
for row in event.rows:
if event.table == 'users':
user_id = row['after_values']['id']
redis_key = f"user:{user_id}"
self.redis.setex(redis_key, 3600, json.dumps(row['after_values']))
def handle_delete_event(self, event):
"""处理删除事件"""
for row in event.rows:
if event.table == 'users':
user_id = row['values']['id']
redis_key = f"user:{user_id}"
self.redis.delete(redis_key)
|
五、读写分离场景的一致性
1. 主从延迟问题
解决主从延迟导致的脏读:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| def get_user_with_read_after_write(user_id, write_timestamp=None):
"""
读写分离环境下的一致性读取
"""
if write_timestamp:
slave_lag = get_slave_lag()
if time.time() - write_timestamp < slave_lag + 1:
return read_from_master(user_id)
user_data = read_from_slave(user_id)
if user_data:
return user_data
return read_from_master(user_id)
def read_from_master(user_id):
"""从主库读取"""
user_data = db_master.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", user_id)
if user_data:
redis.setex(f"user:{user_id}", 3600, user_data)
return user_data
def read_from_slave(user_id):
"""从从库读取"""
return db_slave.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", user_id)
def get_slave_lag():
"""获取从库延迟"""
result = db_slave.query("SHOW SLAVE STATUS")
return result['Seconds_Behind_Master'] if result else 0
|
六、监控与治理
1. 一致性监控体系
监控关键指标:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| class ConsistencyMonitor:
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = {
'cache_hits': 0,
'cache_misses': 0,
'stale_reads': 0,
'consistency_errors': 0
}
def check_consistency(self, key, db_data, cache_data):
"""检查数据一致性"""
if db_data != cache_data:
self.metrics['consistency_errors'] += 1
self._repair_inconsistency(key, db_data)
return False
return True
def _repair_inconsistency(self, key, correct_data):
"""修复不一致数据"""
try:
redis.setex(key, 3600, correct_data)
logging.warning(f"Repaired inconsistency for key: {key}")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to repair inconsistency: {e}")
def track_stale_read(self, key, duration):
"""跟踪过期数据读取"""
self.metrics['stale_reads'] += 1
if duration > 5:
send_alert(f"Stale data detected: {key}", f"Duration: {duration}s")
def generate_report(self):
"""生成监控报告"""
total_requests = self.metrics['cache_hits'] + self.metrics['cache_misses']
consistency_rate = 1 - (self.metrics['consistency_errors'] / total_requests) if total_requests > 0 else 1
return {
'consistency_rate': f"{consistency_rate:.3%}",
'stale_reads': self.metrics['stale_reads'],
'total_requests': total_requests
}
|
2. 自动修复机制
不一致数据自动检测和修复:
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| class AutoRepairService:
def __init__(self, redis_client, db_client):
self.redis = redis_client
self.db = db_client
self.repair_queue = queue.Queue()
self.start_workers()
def start_workers(self):
"""启动修复工作线程"""
for i in range(3):
thread = threading.Thread(target=self._repair_worker)
thread.daemon = True
thread.start()
def _repair_worker(self):
"""修复工作线程"""
while True:
try:
key = self.repair_queue.get()
self._repair_key(key)
self.repair_queue.task_done()
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Repair worker error: {e}")
def _repair_key(self, key):
"""修复单个key"""
if key.startswith('user:'):
user_id = key.split(':')[1]
db_data = self.db.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", user_id)
if db_data:
self.redis.setex(key, 3600, db_data)
def schedule_repair(self, key):
"""调度修复任务"""
self.repair_queue.put(key)
def bulk_repair_check(self, pattern="user:*"):
"""批量检查修复"""
cursor = 0
while True:
cursor, keys = self.redis.scan(cursor, match=pattern, count=100)
for key in keys:
self._verify_and_repair(key)
if cursor == 0:
break
def _verify_and_repair(self, key):
"""验证并修复数据"""
cache_data = self.redis.get(key)
if not cache_data:
return
if key.startswith('user:'):
user_id = key.split(':')[1]
db_data = self.db.query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = %s", user_id)
if db_data != cache_data:
self.schedule_repair(key)
|
七、场景化解决方案
1. 电商商品库存一致性
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| class InventoryService:
def __init__(self):
self.redis = redis.Redis()
self.db = database.Connection()
self.lock = redis.Redis()
def decrease_stock(self, product_id, quantity):
"""减少库存(保证一致性)"""
lock_key = f"lock:stock:{product_id}"
cache_key = f"stock:{product_id}"
with self._acquire_lock(lock_key):
cache_stock = self.redis.get(cache_key)
if cache_stock and int(cache_stock) < quantity:
raise Exception("库存不足")
self.db.update(
"UPDATE products SET stock = stock - %s WHERE id = %s AND stock >= %s",
quantity, product_id, quantity
)
if cache_stock:
new_stock = int(cache_stock) - quantity
self.redis.setex(cache_key, 3600, str(new_stock))
else:
self.redis.delete(cache_key)
return True
def get_stock(self, product_id):
"""获取库存信息"""
cache_key = f"stock:{product_id}"
stock = self.redis.get(cache_key)
if stock:
return int(stock)
stock = self.db.query("SELECT stock FROM products WHERE id = %s", product_id)
if stock is not None:
self.redis.setex(cache_key, 3600, str(stock))
return stock
def _acquire_lock(self, lock_key, timeout=10):
"""获取分布式锁"""
identifier = str(uuid.uuid4())
end = time.time() + timeout
while time.time() < end:
if self.lock.set(lock_key, identifier, nx=True, ex=5):
return identifier
time.sleep(0.1)
raise Exception("获取锁超时")
|
2. 金融账户余额一致性
python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| class AccountService:
def __init__(self):
self.redis = redis.Redis()
self.db = database.Connection()
def transfer(self, from_account, to_account, amount):
"""转账操作(强一致性要求)"""
with self.db.transaction():
self.db.update(
"UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance - %s WHERE id = %s AND balance >= %s",
amount, from_account, amount
)
self.db.update(
"UPDATE accounts SET balance = balance + %s WHERE id = %s",
amount, to_account
)
self.redis.delete(f"account:{from_account}")
self.redis.delete(f"account:{to_account}")
self._log_transaction(from_account, to_account, amount)
return True
def get_balance(self, account_id):
"""获取余额(最终一致性)"""
cache_key = f"account:{account_id}"
balance = self.redis.get(cache_key)
if balance:
return decimal.Decimal(balance)
balance = self.db.query("SELECT balance FROM accounts WHERE id = %s", account_id)
if balance is not None:
threading.Thread(
target=self.redis.setex,
args=(cache_key, 300, str(balance))
).start()
return balance
|
八、总结与最佳实践
一致性方案选择指南

最佳实践 checklist ✅
设计阶段:
明确业务的一致性要求
选择合适的一致性级别
设计缓存更新策略
规划监控和修复机制
开发阶段:
实现适当的重试机制
添加分布式锁避免并发冲突
设置合理的超时时间
实现数据验证和修复
运维阶段:
监控缓存命中率和一致性
设置告警机制
定期进行一致性检查
准备应急预案
关键建议 🚀
不要过度设计:根据业务需求选择适当的一致性级别
监控重于预防:建立完善的监控体系比追求完美方案更重要
设计容错机制:假设不一致会发生,准备好修复方案
持续优化改进:根据监控数据不断调整和优化策略
通过本文的详细分析和实践方案,你应该能够根据业务需求选择合适的缓存一致性方案,并构建出可靠的数据同步体系。记住:一致性是一个持续的过程,而不是一次性的解决方案!