蒙特卡洛算法是一个基于几何概率模型的近似估计真实值的方法,可以近似估计出圆周率π和一些被积函数比较复杂不容易求出积分的积分值。
近似估计出圆周率π举例:

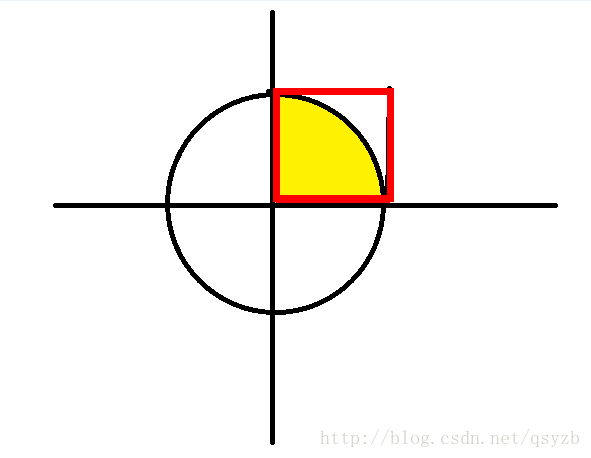
假设在正方形内投掷随机点数量为N(N∈N*),则按几何概率,当N很大时,落在圆中数量为n(n∈N*), 而N与n的比值等价于两者的面积比,即:
πr²/4r²= n/N
=> π = 4n/N
C++代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| #include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <cmath>
const double r = 2;
double Random(int min, int max);
class location {
public:
double x, y;
location(double x, double y) {
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
location() {
this->x = Random(0, 2 * r);
this->y = Random(0, 2 * r);
}
};
double Random(int min, int max) {
double random_number = (double)std::rand() / RAND_MAX;
int integer_part = std::rand() % max;
double result = static_cast<double>(integer_part) + random_number;
return result;
}
double GetPai(int N) {
location center(r, r);
int n = 0;
for(size_t i = 0; i < N; i++) {
location happen;
bool ifCircle = pow((happen.x - center.x), 2) + pow((happen.y - center.y), 2) <= pow(r, 2);
ifCircle&& n++;
}
double Pai = (double)4 * n / N;
return Pai;
}
int main() {
int N;
while(true) {
std::cout << "请输入蒙特卡洛试验次数:" << std::endl;
std::cin >> N;
double pai = GetPai(N);
std::cout << "PAI计算结果为:" << std::endl << pai;
std::cout << Random(1, 10)<<std::endl;
}
}
|
运行结果: